Innovations in technologies made the resources cheaper than earlier. This enables organizations to store more data at lower cost and thus increasing the size of data.
Gradually the size of data becomes bigger and now it moves from Megabytes (MB) to Petabytes (1e+9 MB).
This huge increase in data requires some different kind of processing. This enormous size also requires a change in the ways of storage than the traditional one because the traditional one was not built for such scenario.
In order to get a solution, the definition of Big Data evolved.
The Technology:
Big Data is not a single technology or techniques. This is a broad term for a data sets which is so large or complex that traditional data processing applications are inadequate to process it.
It refers to data creation, storage, retrieval and analysis that is remarkable in terms of its four elements.
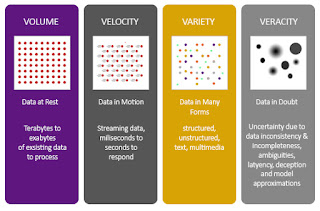
These four elements are known as 4V’s of Big Data :
- Volume
- Velocity
- Variety
- Veracity
The details of these elements is explained one by one.
The Elements (4V’s of Big Data):
VOLUME:
Remember the days of 20th century when 10 GB of storage for a PC was enough.
In today’s world a typical flight can generate 5-6 GB of data every second. With this ratio a trip of 10 to 12 hours can generate 500 Terabytes of data.
Even social websites like Facebook, twitter, YouTube are adding thousands of terabytes of data every day. 40 Zettabyte of data is expected to created by 2020 which is a 300 times from 2005.
VELOCITY
The high speed generated data also needs to be processed with the same speed with ZERO error for analysis.
For example, data generated by flight needs to be analyzed with the same speed and without any fault. A delay of even a millisecond can cost life of passengers.
In the same way high frequency stock trading reflects market changes in milliseconds and a single error can lead economy to damage severely.
A modern car is having close to 100 sensors that monitors items like fuel, tire pressure etc.
VARIETY:
Traditional database systems were designed to address smaller volumes of structured data, a predictable and consistent data structure whereas Big Data isn’t about just structured data.
Big Data is also includes Geo spatial data, 3-D data, audio and video, and unstructured data which including log files from various systems like flights, exchanges and social media.500 Million tweets per day,
30 Billion of contents every months, 4 Billion of hours of Video are watched each month on YouTube are an example of different forms of data
VERACITY:
It is the 4th V of 4V’s of Big Data. It is biases, noise and abnormality in data.
In every analytic processing, 40-60% of time is spent on “data preparation” phase like removing duplicates, partial entries, removing null or blank, aggregating results etc.
Uncertainty of data (poor data quality) causes $1.3 Trillion loss to US economy.
Every 3rd business leaders do not trust the data they use to make decision. Hence, with respect to save processing time and accuracy of processed data this V is very important.
Tools/Technologies of Big Data:
As multiple technologies and techniques involved in Big data, numerous tools are available which usages different technologies.
For Example, Giraph or Hema or GraphX are using Graph Model technology. Hadoop or HaLoop or Twister usages MapReduce technology. Pig or Tez or Hive usages MapReduce as well as DAG Model both.
Other tools and technologies are also in the market for the same objective.
Hence, an organization should take utmost care while selecting a Big Data technology based on their data processing requirements.
Data processing Requirements:
The data processing requirements of organization can be :
- Operational(Real time, Interactive workloads): low latency response on highly selective access criteria, Supported by NoSQL like MongoDB.
- Analytical (High throughput): Complex queries, touches most of the data, supported by MPP database systems and MapReduce.
Decision Making Factors:
Decision makers must consider 6 point agenda before deciding a technology for their organization.
- Online vs. Offline Big Data
- Software Licensing Models
- Community
- Developer Appeal
- Agility
- General Purpose vs. Niche Solutions
Choosing a way which provides both types of abilities to an organization becomes easy with the new technologies.
NoSQL, MPP databases, and Hadoop have emerged to address Big Data challenges. However, all of them are designed to solve one problem only.
Therefore, to solve this complex problem companies are leveraging multiple tools integrated to each other. For example integration of a NoSQL database such as MongoDB with Hadoop.
Gradually Hadoop becomes an important ingredient of Big Data Technologies by its usability, scalabilities and capabilities. Moreover, it is open source and easy to configure with other Big Data tools.

Thanks, great article.
I absolutely love your website.. Pleasant colors
& theme. Did you develop this web site yourself? Please reply
back as I’m hoping to create my own site and want to find out where you
got this from or exactly what the theme is called. Thanks!
Hi,
I am happy that you liked it. I have done by myself. I took help of one of my friend.
This was result of googling 🙂
Theme is Zerif light
Thank you
yes. I did it myself
When I originally left a comment I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments
are added- checkbox and from now on each time a comment is added I
get four emails with the exact same comment. Perhaps there is a way you can remove
me from that service? Thanks a lot!
Hi there just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you
know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue.
I’ve tried it in two different browsers and both show the same results.